Industrial automation is transforming industries worldwide. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global industrial automation market is expected to reach $296.70 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.2%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for efficiency and productivity in various sectors, from manufacturing to energy.
Automation technologies enhance precision and reduce human error. Companies are adopting robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline operations. A study by McKinsey reveals that automation could increase productivity by up to 40% in certain industries. Such advancements can lead to significant cost savings and improved product quality.
However, the rise of industrial automation raises questions. Job displacement is a real concern. Workers may face challenges in adapting to new technologies. Additionally, dependence on automated systems can lead to vulnerabilities. Addressing these issues is crucial for a balanced approach to automation in the workplace.
Industrial automation refers to the use of technology to control and manage production processes. This includes machinery, control systems, and information technologies. By automating tasks, industries can improve efficiency and reduce human error. Automation systems often consist of sensors, actuators, and computing devices. These elements work together to streamline operations.
The scope of industrial automation is broad. It covers various sectors like manufacturing, energy, and logistics. Machines can perform repetitive tasks with precision. For example, in manufacturing, robotic arms assemble products rapidly. However, there are challenges. Dependence on technology can lead to job displacement. Workers may need retraining to adapt to these changes.
Moreover, not every automation project succeeds. Implementation might face resistance from staff. Integration with existing systems can also be problematic. Companies must plan carefully. They should consider not just efficiency but human factors as well. Balancing technology with the workforce is crucial for long-term success.
Industrial automation refers to using technology to control production processes. Key components include sensors, actuators, and control systems. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global industrial automation market is expected to grow from $175 billion in 2020 to over $300 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for efficiency and productivity.
Sensors play a crucial role in automation. They collect data about the production environment, such as temperature and pressure. Actuators convert control signals into physical motion. Together, they provide feedback loops that improve system performance. Control systems analyze this data and make real-time adjustments, fostering precision. It's worth noting, however, that reliance on technology may sometimes lead to system failures, which can disrupt production.
Tips: Regularly check sensor calibrations to maintain accuracy. Limit the complexity of systems; simplicity often leads to greater reliability. Robust training for operators is essential. Automation does not replace human oversight. In fact, experienced personnel are vital for interpreting data and making crucial decisions.
| Component | Description | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) | A digital computer used for automation of electromechanical processes. | Ladder Logic, Function Block Diagram |
| Human-Machine Interface (HMI) | Software or hardware that allows interaction between operators and machines. | Touchscreen displays, SCADA systems |
| Sensors | Devices that detect changes in the environment and provide data to the PLC. | Proximity sensors, Pressure sensors, Temperature sensors |
| Actuators | Mechanical devices that convert energy into motion to control systems. | Electric motors, Hydraulic cylinders |
| Industrial Robots | Robotic arms used for repetitive tasks like welding, assembly, and packaging. | Articulated robots, SCARA robots, Delta robots |
| Control Systems | Systems used to manage, command, direct, or regulate the behavior of other devices. | PID controllers, Distributed Control Systems (DCS) |
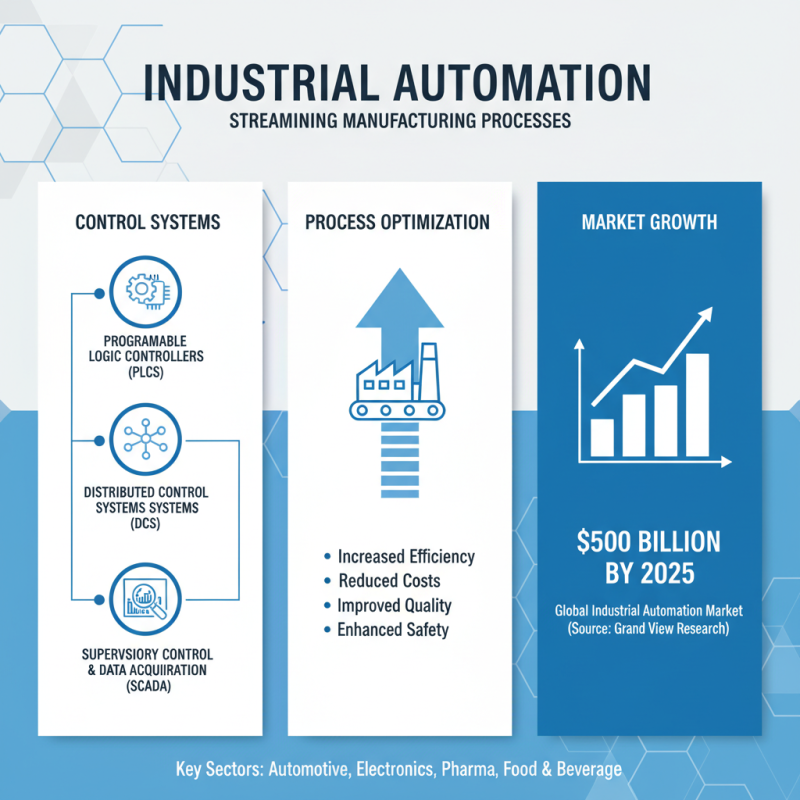
Industrial automation streamlines manufacturing processes by using various control systems. These systems can include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) technologies. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global industrial automation market is projected to reach $500 billion by 2025, reflecting its growing significance in diverse sectors.
The control systems operate through sensors, actuators, and software applications that monitor and manage production lines. For example, sensors detect variables like temperature and pressure, which inform the systems to trigger necessary actions. With advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT), real-time data sharing becomes possible. This enhances efficiency and minimizes downtime. Nevertheless, the initial setup costs can be high and system integration may face many challenges. Many companies struggle to keep pace with rapid technology changes.
Training staff to work with advanced automation systems is crucial yet often overlooked. A survey by McKinsey indicates that 60% of companies report difficulties in integrating new technologies due to workforce readiness issues. As industries move towards higher levels of automation, the need for skilled labor becomes increasingly apparent. Failure to address these challenges can leave businesses at a competitive disadvantage.
Industrial automation is transforming industries worldwide. It streamlines operations and improves efficiency by using advanced technologies. Companies implement automated systems to reduce costs and minimize human error. This leads to faster production rates and consistent quality.
The benefits are significant. First, automation enhances productivity. Machines can operate 24/7, completing tasks quicker than humans. This results in higher output with fewer resources. Next, safety improves in workplaces. Dangerous tasks can be handled by machines, reducing worker injury risks. However, the initial investment can be daunting for some companies.
Despite these advantages, challenges exist. Skilled labor requirements may shift, creating gaps. Workers may need retraining, which can strain resources. Companies must balance automation with human jobs. Finding this equilibrium is crucial for sustainable growth in a rapidly changing environment.
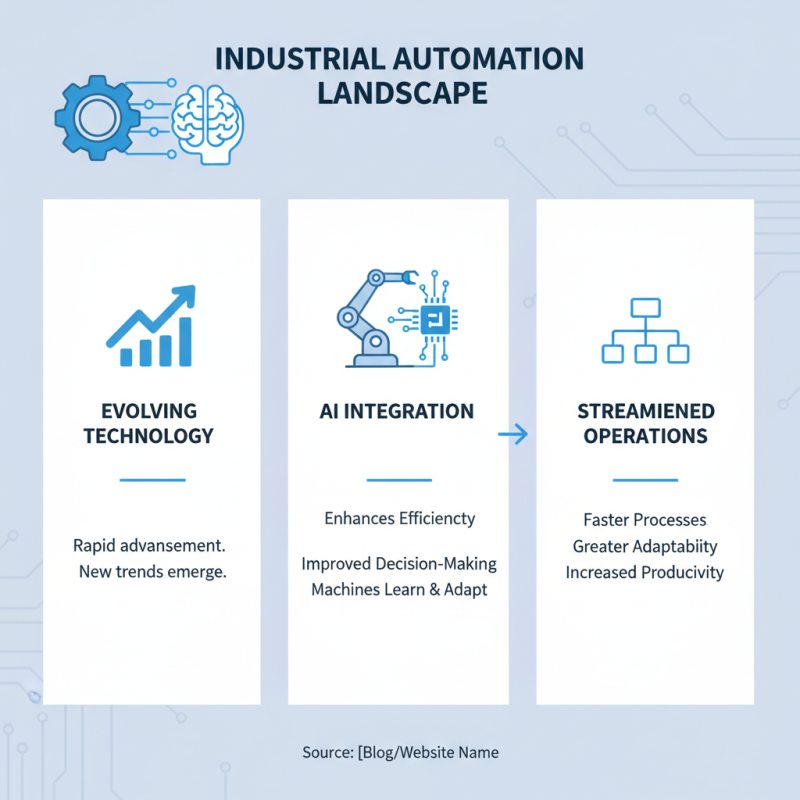
The landscape of industrial automation is rapidly evolving. As technology advances, new trends emerge. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI enhances efficiency and decision-making processes. Machines can learn and adapt to various tasks. This leads to more streamlined operations.
Another area of growth is the adoption of robotics. Robots are becoming more sophisticated and versatile. They perform intricate tasks with precision. However, reliance on robotics raises questions. Are we losing human touch in manufacturing? Balancing automation and human jobs is essential. This ongoing dialogue fuels innovation.
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role too. It connects machines and systems. Data flows in real-time, offering insights for optimization. Yet, security concerns persist. Vulnerabilities in systems can lead to breaches. Companies must prioritize cybersecurity measures. The future of industrial automation is promising but complex, inviting both excitement and caution.







