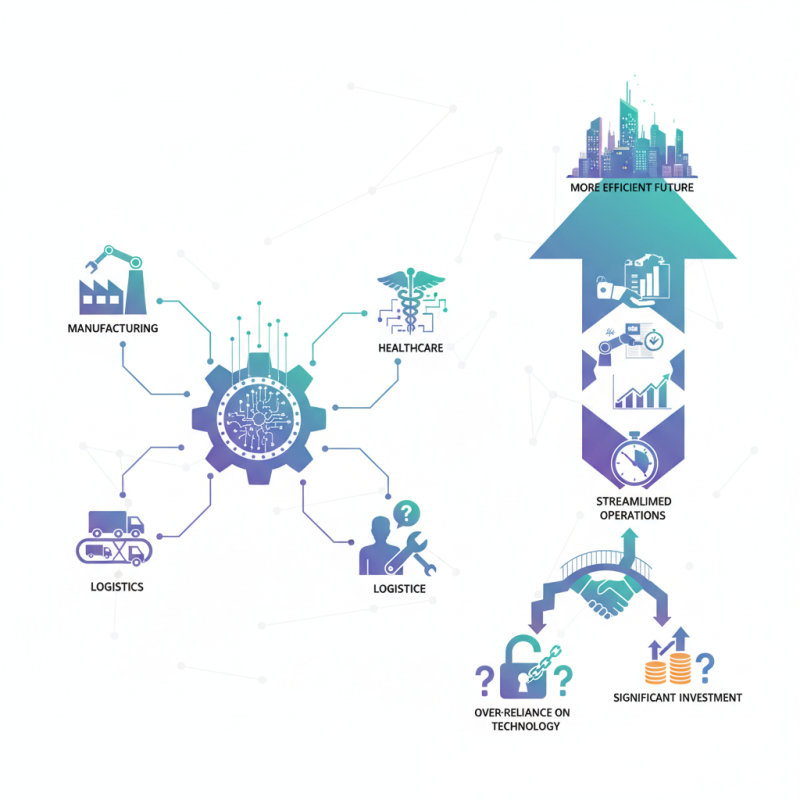
Automation engineering is revolutionizing the way industries operate. This field combines technology and engineering principles. It aims to automate processes and improve efficiency. The impact of automation engineering can be seen across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. These advancements reduce human error and streamline operations.
However, the rise of automation engineering brings challenges. Workers may face job displacement due to increased automation. There are concerns about over-reliance on technology. Companies must ensure that automation is implemented thoughtfully. Balancing innovation with the human element is crucial.
Furthermore, while automation offers many benefits, it may also require significant investment. Some organizations struggle to keep pace with rapid advancements. They may find it challenging to adopt new technologies. Despite these obstacles, automation engineering continues to transform industries, paving the way for a more efficient future. It encourages ongoing conversations about the relationship between technology and the workforce.
Automation engineering is a dynamic field that focuses on designing and implementing automated systems. It integrates concepts from electrical, mechanical, and software engineering. Engineers in this area develop solutions that enhance efficiency and reduce human error. For example, they may work on robotics, control systems, or industrial process automation.
Tips: When exploring automation, consider the specific industry needs. A tailored approach can yield better results.
In practice, automation engineering transforms workflows. Tasks such as assembly line operations are streamlined. Machines can perform repetitive tasks faster than humans. This increases productivity but requires a careful balance. Over-reliance on automation can lead to a loss of skilled positions.
Tips: Always assess the long-term impact of automation on the workforce. Implementing retraining programs can help mitigate job displacement.
While automation offers numerous benefits, it comes with challenges. For instance, maintenance of automated systems can be complex. Engineers must ensure reliability and efficiency. This means continuous monitoring and improvement of systems. Embracing automation is an ongoing journey.
Automation engineering is a field that integrates technology to enhance productivity. It facilitates the design and management of systems that operate processes automatically. Key principles in automation engineering include control systems, robotics, and artificial intelligence. These components work together to improve efficiency and reduce human intervention in various industries.
Control systems play a vital role in ensuring processes run smoothly. They use sensors to gather data and feedback mechanisms to manage operations. Robotics, on the other hand, allows for precision and repeatability in manufacturing tasks. These machines can be programmed to perform specific duties, often exceeding human capabilities. Artificial intelligence further enhances automation by enabling systems to learn and adapt over time.
Despite its advantages, automation raises concerns. Job displacement is a significant issue as machines replace human workers. Additionally, there's a risk of over-reliance on technology, which can lead to vulnerabilities. Developing strategies to manage these challenges is essential. The balance between automation and human involvement is crucial for sustainable progress.
| Dimension | Description | Technologies Used | Industries Impacted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Automation | Streamlining repetitive tasks to improve efficiency. | Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Control Systems | Manufacturing, Finance |
| Industrial Automation | Integration of machines and control systems for manufacturing. | Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), SCADA Systems | Automotive, Food & Beverage |
| Building Automation | Management of HVAC, lighting, security, and other systems. | Building Management Systems (BMS), IoT Devices | Commercial Real Estate, Smart Homes |
| Test Automation | Automating testing of software applications for quality assurance. | Test Automation Frameworks, Scripting Tools | Information Technology, Software Development |
| Supply Chain Automation | Optimizing supply chain operations through advanced technologies. | AI, Machine Learning, Blockchain | Retail, Logistics |
Automation engineering plays a significant role in various industries, reshaping how businesses operate. In manufacturing, for example, automated systems can improve production efficiency by 30% or more. This transformation helps reduce costs and minimize human error. Yet, there are challenges. Workers face job displacement, and retraining programs must evolve to address this issue effectively.
In the energy sector, automation enhances monitoring and control processes. Reports indicate that automated systems can improve energy efficiency by up to 20%. This reduction is crucial as industries strive to meet sustainability goals. However, integrating new technologies raises concerns about cybersecurity and system failures, which can lead to serious disruptions.
Meanwhile, in healthcare, automation streamlines patient management and diagnostics. Studies show that automation can decrease administrative tasks by 50%. Still, over-reliance on technology may compromise human interaction in patient care. This opens a dialogue about balancing efficiency and the essential human touch in healthcare delivery.
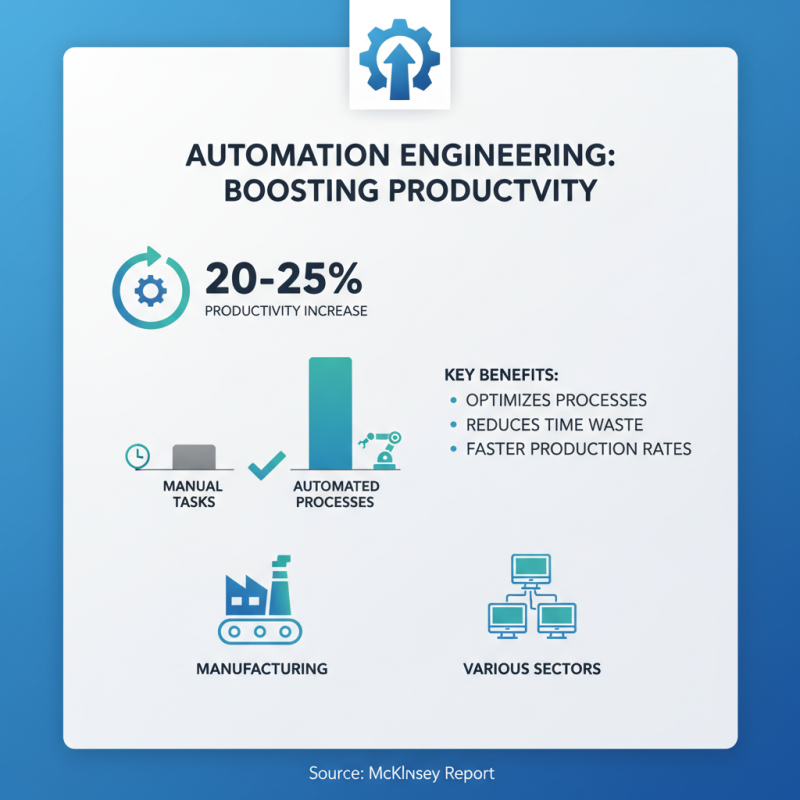
Automation engineering is revolutionizing productivity and efficiency across various industries. A report from McKinsey indicates that automation can increase productivity by 20 to 25% in many sectors. This shift allows companies to optimize key processes, cutting down on time wasted on manual tasks. For example, in manufacturing, automation reduces assembly time significantly, allowing for faster production rates.
However, these advancements come with their own set of challenges. A rise in automation can lead to workforce concerns. Many workers fear job loss as machines take over roles traditionally held by humans. The World Economic Forum reports that 85 million jobs may be displaced by 2025 due to automation. This disruption prompts industry leaders to reconsider employee training and workforce restructuring.
Despite these concerns, the benefits remain significant. A study by Deloitte indicates that automating routine tasks can boost overall efficiency by nearly 30%. Employees can then focus on more strategic tasks, leading to innovative breakthroughs. Balancing automation's advantages with workforce implications requires thoughtful implementation. It's essential for industries to adapt, ensuring both productivity and personnel welfare are prioritized in this transformative era.
Automation engineering is rapidly evolving, driving significant changes across various industries. Trends indicate a shift towards more intelligent systems. By 2025, the global market for automation is expected to exceed $200 billion. This growth highlights the urgency for businesses to adopt advanced automation solutions.
Yet, challenges persist. Many companies face a skills gap in automation technology. According to a recent survey, 70% of firms report difficulty in finding qualified professionals. This shortage can hinder the effective implementation of automation projects. Additionally, integrating new technologies often encounters resistance from employees. They may fear job displacement or struggle to adapt. Such issues require careful management and communication.
Cybersecurity is another area of concern. Increased automation introduces more digital entry points. Reports suggest that 30% of attacks target automated systems. Without proper safeguards, companies could face serious risks. Balancing innovation with security demands is crucial. Industry leaders must continually assess and refine their strategies to foster a safe and efficient automation landscape.







