The manufacturing automation landscape is rapidly evolving. A recent report by PwC indicates that 70% of manufacturers are investing in automation technologies. This trend is reshaping operational efficiency and productivity across the sector. Experts in the field, such as Dr. Emily Carter, emphasize the importance of adaptation. She stated, “Embracing innovation in manufacturing automation is no longer optional; it's critical for survival.”
Amid these advancements, challenges persist. The integration of robotics and AI presents both opportunities and hurdles. For instance, workers may feel threatened by automation adoption. According to a study by McKinsey, approximately 30% of jobs in manufacturing could be automated by 2030. While this can streamline processes, it raises questions about workforce displacement. Addressing these concerns is essential for a holistic approach to manufacturing automation.
Investments in smart factories and IoT are on the rise. However, not all companies are equipped to adapt to these changes. Many struggle with the pace of technological advancement. As the industry continues to evolve, the need for a strategic framework becomes clear. It is vital for businesses to assess their readiness for the future of manufacturing automation.

The manufacturing automation landscape is evolving rapidly. By 2026, key technologies are set to transform the industry significantly. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global market for industrial automation is projected to reach $296.70 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.25%. This growth hints at a massive shift in how factories operate and manage production.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of this transformation. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to improve efficiency. Predictive maintenance, driven by AI, has the potential to reduce downtime by about 50%. However, the integration of AI poses challenges. Many organizations struggle with workforce adaptation and retraining. Cybersecurity also emerges as a major concern as automation increases data vulnerability.
Robotics continues to play a crucial role in automation. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human workers. They enhance productivity, but their implementation can lead to job displacement anxiety among employees. Moreover, while automation offers operational advantages, it can create complexities in supply chain management. Businesses must address these challenges while leveraging the advantages of new technologies.
Manufacturing automation is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by advancements in AI and machine learning. According to recent reports, automation technologies are expected to boost productivity by up to 30% by 2026. This reveals a significant trend towards integrating intelligent systems into manufacturing workflows. Factories are now leveraging AI to analyze real-time data, improving decision-making by up to 25%.
Machine learning models enhance production lines by predicting equipment failures. These models can decrease downtimes by as much as 20%. However, the reliance on such technology raises concerns. There are still challenges in data privacy and the accuracy of algorithms. Not all companies can adapt quickly to these innovations, leading to uneven progress across the industry.
Despite the benefits, skills gaps persist. Workers must be trained to collaborate effectively with machines. Approximately 70% of manufacturers cite the need for upskilling their workforce. Addressing this issue is vital for maximizing the potential of AI in production. The journey of adopting automation is not without obstacles, requiring careful consideration and strategic planning.
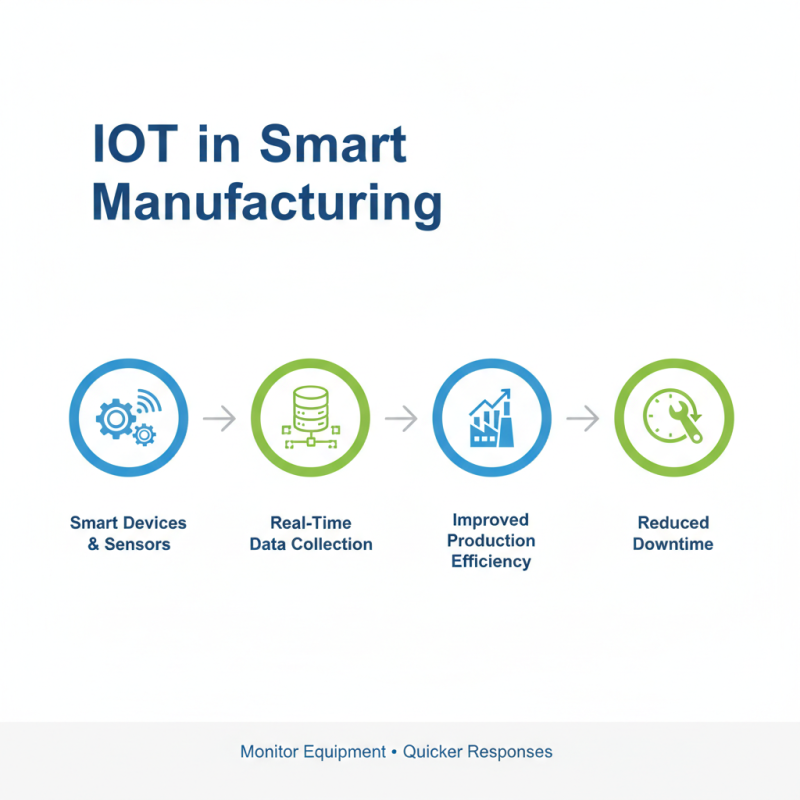
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a critical role in smart manufacturing. Smart devices and sensors collect real-time data. This data helps improve production efficiency. Manufacturers can monitor equipment performance closely. This leads to quicker responses to issues. It reduces downtime significantly.
However, integrating IoT is not without challenges. Many factories lack the necessary infrastructure. Legacy systems can complicate new tech adoption. Employees may resist change, fearing job loss. These issues need addressing for successful implementation. Security risks also arise with increased connectivity. Ensuring data integrity is vital in the manufacturing environment.
Despite these concerns, the potential benefits are enormous. IoT can create more agile production lines. Predictive maintenance can save costs and time. As manufacturers embrace these innovations, they will need to adapt continuously. Balancing technology with workforce dynamics is essential. The journey toward smart manufacturing is just beginning.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus in the manufacturing automation industry. According to a recent report by McKinsey, over 70% of manufacturers are prioritizing sustainability initiatives. This shift is reshaping production processes and technologies. Companies are integrating energy-efficient systems to reduce waste and emissions. For instance, smart sensors now optimize energy consumption in real time.
However, the journey is not without challenges. Many manufacturers face high initial costs for sustainable technology. The transition may disrupt existing operations. Reports indicate that around 25% of companies struggle with adopting new technologies. This gap in adaptation can hinder overall progress in the industry.
Moreover, regulatory pressures are increasing. The International Energy Agency projects that compliance costs could rise by 30% in the coming years. This forces manufacturers to rethink their sustainability strategies. Some may resort to quick fixes rather than long-term solutions. This approach could lead to short-lived improvements. Careful planning and investment are essential for meaningful change in the sector.

The manufacturing automation landscape is rapidly changing. As technology evolves, so does the workforce. Upskilling has become essential for workers to thrive in this automated environment. Many employees face challenges when adapting to new tools and robotics. Training programs are becoming more relevant but often lack depth.
Workers must learn not just to operate machines but also to understand the underlying technology. This knowledge enables them to troubleshoot and innovate. Workshops and on-the-job training can bridge the gap. Yet, not all programs address the unique needs of each worker. A one-size-fits-all approach often leads to disengagement.
Moreover, companies sometimes overlook the importance of soft skills. Communication and critical thinking are crucial in a tech-driven workspace. Focusing solely on technical skills may create a disconnect. Balancing both aspects can lead to a more adaptable workforce. The path forward is clear; investing in comprehensive training will define the future of manufacturing.